Different types of batteries play a pivotal role in substations and the power sector. Lead-acid batteries, with their reliability and cost-effectiveness, are commonly used for backup power in substations to maintain operation during outages. Nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries, known for their durability and wide temperature tolerance, are ideal for critical power backup applications. Lithium-ion batteries, gaining popularity for their high energy density and longer life cycle, are revolutionising energy storage in the power sector, enabling better grid stability and integration of renewable energy sources. Each type of battery contributes to ensuring a reliable and stable power supply, which is crucial for the efficient functioning of substations and the broader power sector.
However, over time, battery capacity can significantly decrease before reaching its expected lifespan due to various factors. To continually assess the health of battery banks, regular maintenance inspections and testing are essential. Among the most effective methods is conducting discharge tests on batteries, allowing us to accurately gauge their remaining capacity. In one of our previous blog we have mentioned about Estimate Residual battery life with ideal battery discharge kit also in our last blog we have mentioned about the IEC standards that guide this testing procedure – Understanding IEEE Standards for Battery Discharge Testing
By proactively monitoring battery health through discharge testing, we can optimize performance, prevent unexpected failures, and maintain reliable backup power for critical systems.
Connection
- Ensure the Battery Bank is fully charged before testing. Disconnect the Battery Bank from the Charger and all other loads.
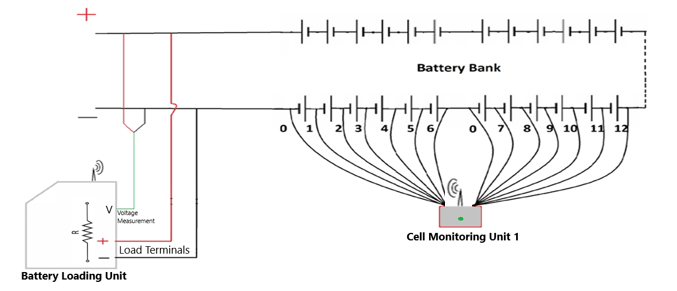
- Connect earthing cable to Master Earthing Terminal of Battery Loading Unit.
- Connect Load Terminals to positive and negative terminals of Battery Bank using suitable cables.
- Connect voltage measurement leads to Battery Bank terminals.
- Connect Cell Monitoring devices to individual cells in sequence, as per the markings given on test leads.
- Connect wireless antenna to main Battery Loading Unit for wireless communication with PC and Cell monitoring devices.
- Connect 230V AC Mains supply using Mains Cord to Battery Loading Unit.
Operation
- Check connectivity between Cell Monitoring Devices and the main Battery Loading Unit.
- Ensure safety precautions are followed.
- Record baseline data (initial battery capacity in Ah, cell and string voltage, and C Rating or discharge current).
- Calculate the discharge current, time, electrical critical voltage using formulas mentioned below:
- Battery Bank Specification:
- Voltage = Cell Voltage x No of Cells in Series
- Capacity = Cell Capacity x No of Strings in parallel (Ah)
- Discharge Current= Capacity in Ah / C rating
- Discharge Time= Capacity in Ah / Discharge Current
- Electrical critical voltage (ECV) or end voltage of a Cell or Battery Bank (if not specified by OEM): ECV= 0.9 x Nominal Voltage
- Monitor voltage, current, and time during the discharge process.
Interpretation
- Calculate the remaining capacity of the Battery Bank.
- Compare the remaining capacity with the manufacturer’s rated capacity and previous results.
- Assess the battery’s health and degradation.
- If capacity falls significantly, consider a replacement.
- Detect weak cell and faulty intercell connectors and replace them.
Conclusion
SCOPE’s battery loading units are ideal for controlled and monitored discharge of batteries. The kit is essential for optimizing the battery performance and maximizing the utilization of the battery by extending the life of the battery. To know more, please visit https://www.scopetnm.com/test-and-measurements/dc-test-equipment/battery-loading-unit or write to us at marketing@scopetnm.com

