In our previous blog on Dissolve Gas Analysis, we threw the light on basics of DGA like causes of gas formation, types of DGA and various methods used for DGA analysis. In this blog, we will discuss in detail Gas extraction methods and analysis methods.

Gas extraction from DGA:
While conducting a DGA test on the oil sample it is important to extract all the available gasses in the sample. There are three main methods used for gas extraction
- Headspace Extraction
- Membrane Extraction
- Vacuum Extraction
- Headspace Extraction Method:
The headspace method is used to extract gasses and it is a conventional method in which the gas fumes present in the headspace of the oil sample container are extracted in the gas chamber (as shown in Fig. 1). This method is used by most DGA analyzers as it is most cost-efficient. This method is dependent on the solubility constant which is also known as the Ostwald coefficient. During the headspace extraction method, the concentration of gas can be calculated from only partly extracted gasses by using the Ostwald coefficient. The coefficients are different for different gasses and dependent on temperature, oil quality, and base oil type like synthetic oil, mineral oil, easter oil etc. The main disadvantage of this method is that the measurement uncertainty can be observed related to differences in the coefficients
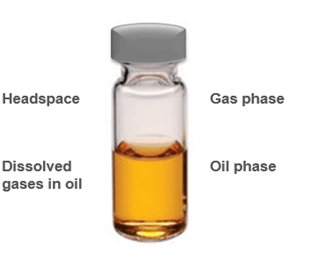
*Photo Credit: https://www.vaisala.com/en
- Membrane-based extraction method:
In the membrane base method, a gas-permeable membrane is used to extract the gasses from the oil sample. A lot of studies have been conducted aiming at membrane modification to obtain better separation performance. It cannot be ignored that the conditions of oil also affect the performance of membranes. Most of the online DGA’s using the Photoacoustic Spectroscopy (PAS) principle are using the membrane-based technology for gas extraction. This method is much better than the headspace method as we get more volume of the gas samples, but there are some drawbacks also with this method. There are many possibilities of membrane failure or saturation. Many of the users are facing these issues. Hence it requires frequent maintenance, calibration, and membrane replacement. This will again cause an increase in ownership cost
- Vacuum Extraction Method:
The modest advanced method used for gas extraction is vacuum extraction. In this method gasses are extracted from transformer oil under a partial vacuum, i.e. very low absolute pressure is applied to the oil sample at a controlled temperature. With Vacuum extraction, complete gas separation is carried out to get extracted total quantity of gasses as compared with the traditional headspace or membrane methods. Hence this method is not dependent on the gas solubility in oil volume and more reliable across the various oil ranges. With the partial vacuum extraction, the measurement uncertainty related to differences in the coefficients can be reduced to one-third of that seen with the headspace method.
The advanced new-age online DGAs are not using the vacuum pump. They use the patented method that utilizes the oil column itself as the piston of the cylinder creating the vacuum above the oil level volume by moving the oil with a magnetic gear pump. The oil sample is then sprayed through the vacuum to extract the gasses (As shown in Fig 2). In this method, as there are no mechanical moving parts used, there is no need for any maintenance or service hence the ultimate cost of ownership will be less as compared to other methods.
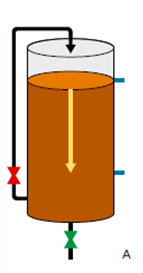
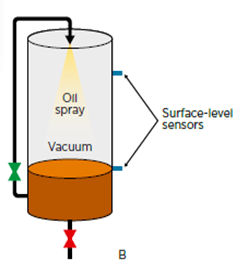
Fig. 2 – Vacuum Extraction. A – Applying a vacuum above the oil level by pumping the oil out. B – Gas is extracted by spraying oil through the vacuum
*Photo Credit: https://www.vaisala.com/en
Gas detection methods
There are various DGA instruments which are divided into three types i.e. laboratory use, portable and online DGA. The methods or technologies used by these DGAs are Gas Chromatography (GC) and Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR). Gas Chromatography is mostly used in the laboratory type DGAs. Whereas, online DGAs use both GC and NDIR.
NDIR method has two different principles i.e. Photo-Acoustic Spectroscopy (PAS) and Transmission NDIR.
Gas Chromatography:
Online DGA monitoring technology was recently introduced. Before that lab testing was the only way to analyze the dissolved gasses in the oil. GC has been used for more than 60 years. Currently, GC analysis is well accepted as the best among DGA techniques to quantify all gasses dissolved in transformer oil including total dissolved gasses (TDG), individual dissolved gasses (IDG) and individual gasses present (IGP) in the gas cuvet due to its better accuracy and less cross sensitivity as compared to other technologies. However, due to the complexity of the equipment required, GC analysis can only be conducted in a laboratory environment.
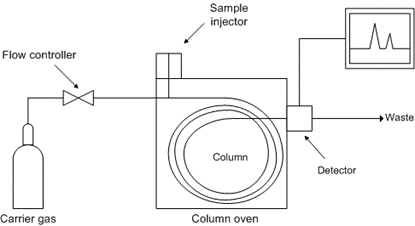
*Photo Credit: https://chem.libretexts.org/
Fig. 3 shows the working of the gas chromatography principle. It consists of a carrier gas system, a sampling system, a separation system, a detection system, and a data recording system. The main components of the carrier gas system are the gas cylinder, flow controller and purification. The carrier gas is a chemically inert gas which carries the extracted gasses through the gas column. The most widely used gasses are Helium and Argon.
The gas sample is injected into the column through the sample injector. Here the components of the Sample is Separated which is one of the crucial parts of Gas Chromatography. The detector monitors the carrier gas as it emerges from the column and generates a signal in response to variations in its composition due to eluted components. As it transmits physical signals into recordable electrical signals, it is another crucial part of GC. This signal is recorded by the recorder.
GC has some advantages also due to which nowadays it is not feasible for field use or online DGA. Maintaining the carrier gas level is the major task while using GC. The inert carrier gasses are generally imported and they are costly ones and also many times not available in advance time. Also, regular maintenance of the gas column and calibration of the detector is essential. There are many other moving parts used in this method hence regular maintenance is required which increases the ultimate cost of ownership.
Photo-Acoustic Spectroscopy (PAS)
Nowadays most online DGA uses the Photo-Acoustic Spectroscopy (PAS) for online DGA monitoring. PAS utilizes spectral analysis to detect the volume of adsorbed gasses based on the photo-acoustic effect. In PAS headspace extraction method is used to extract the gasses from oil samples. Acoustic-based detector used for gas measurement.
The basic principle of PAS is, that extracted fault gasses are collected in the gas caveat and infrared light is passed through it. The gas molecules absorb the light and start vibrating, creating a sound with the caveat walls which is detected by the microphone attached to the walls. The microphone converts the amount of pressure in the electrical signal. Fig. 4 shows the basic operation of PAS
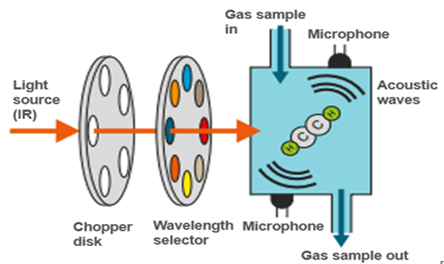
Sound is measured at different wavelengths to record the photoacoustic spectrum. This spectrum is used to identify the fault gasses involved. By using PAS fault gasses such as H2, CO, CO2, CH4, C2H4, C2H2 and C2H6 are detected. PAS is not using any carrier gas for its operation but due to various moving parts and the complex system, it required high maintenance.
Transmission NDIR
Another method working on the infrared absorption technology is transmission NDIR. This is a more advanced and recent method used. When the extracted gas molecules are exposed to the Non-Dispersive InfraRed (NDIR) light, they absorb the energy to get excited. Absorbed wavelength is unique to each gas which forms a gas-specific fingerprint that can be used to identify the gas components in the extracted gas mixture.
The temperature-controlled IR module of the DGA Monitor consists of light sources, band-pass filters, gas cells, mirrors, and detectors. The band-pass filter allows a particular wavelength of light only to pass through.
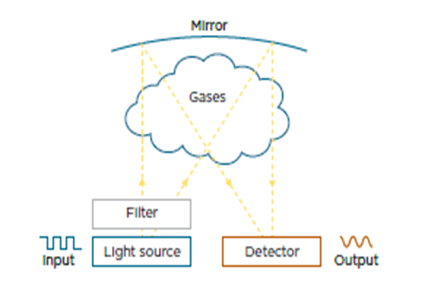
A wide range of IR scanning is done with the help of a tunable filter. The final gas analysis is based on signals gathered using a large wavelength range. All IR sensor elements, including micro glow light sources, filters, and detectors, are micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) made on single-crystal silicon wafers. The wavelength light is absorbed by the gasses the remaining light is collected by the detector and the output spectrum is generated.
Drift Elimination
The absorption properties of the fault gasses do not change over time but signals may still be affected by other factors like contamination of the light source and the detector, the DGA monitor should overcome this drift. In the advanced DGAs internal gas extraction and oil handling mechanisms are built and controlled so that contaminating compounds from the oil cannot gather on the optical surfaces to cause long-term drift. And, care is taken for not allowing any compounds from the ambient air to reach the optics and affect the measurement.
Here the vacuum condition itself is used as the reference measurement. During each measurement cycle wavelength scanning is done in both conditions i.e. with extracted gasses present and then under vacuum. The ratio of these two measurements defines the actual gas concentration the formula used is –
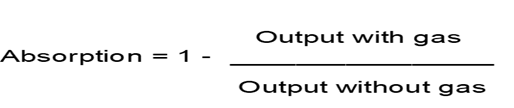
Hence, if there is any drift in the light source intensity then it will not affect the accuracy of the result as the above ratio will remain the same.
Transmission NDIR has good accuracy and repeatability and less cross sensitivity over the PAS. The main advantage is that it does not have any moving parts and does not use any consumables like carrier gas etc. The DGA monitor using the transmission NDIR principle requires very little maintenance as compared to others.
Conclusion
In this blog, we tried to explain methods of gas extraction and Gas analysis and the advantages of Transmission NDIR. Vacuum extraction is the most suitable and useful method for gas extraction and transmission NDIR is the best method for gas analysis considering all the aspects like maintenance cost, calibration, consumables, and overall lifetime ownership cost. SCOPE is offering Vaisala make online DGA using vacuum extraction and transmission NDIR.
For more information about the subject please write to us at marketing@scopetnm.com

